What Type Of Animal Is A Hippo
A recent article posted to thebioRxiv* preprint server illustrated that the activation of the Hippo signaling pathway upon severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection aids the host antiviral response.
 Study: Hippo Signaling Pathway Activation during SARS-CoV-2 Infection Contributes to Host Antiviral Response. Image Credit: NIAID
Study: Hippo Signaling Pathway Activation during SARS-CoV-2 Infection Contributes to Host Antiviral Response. Image Credit: NIAID
Background
SARS-CoV-2 is a zoonotic betacoronavirus that resembles SARS-CoV-like viruses constitute in bats. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by SARS-CoV-2 leads to respiratory failure and damage of various organ systems. Further, the emergence of mutated SARS-CoV-2 variants increases the likelihood of COVID-xix vaccine failure and prolongation of the COVID-19 pandemic, resulting in near 500 meg cases and more than than six million deaths worldwide.
SARS-CoV-two hijacks the host cellular signaling pathways and machinery for viral replication. Yet, the molecular underpinnings of SARS-CoV-2 infection and pathogenesis are poorly understood. Moreover, the in-depth knowledge of molecular pathways of dysregulated signaling circuits might atomic number 82 to new SARS-CoV-two treatment targets.
The authors of the nowadays work previously revealed the essential pathways for SARS-CoV-ii replication, including deoxyribonucleic acid (Deoxyribonucleic acid)-damage response (DDR) pathways, using a library of kinase inhibitors.
About the study
In the nowadays study, the investigators hypothesized and assessed whether the conserved cellular architecture of the Hippo signaling pathway had a role in controlling SARS-CoV-ii multiplication and COVID-19 pathogenesis. This was due to the 1) involvement of the Hippo signaling pathway in immune response, inflammation, and tissue growth and 2) the complex nature of SARS-CoV-2-related immunopathogenesis mechanisms and cell injury.
The authors used SARS-CoV-2-infected lung samples, human main lung air-liquid interface (ALI) cultures, and homo cell models centered on pluripotent stem jail cell-derived cardiomyocytes (PSC-CMs) for the experiments.
The researchers starting time performed the transcriptomic evaluation of ribonucleic acid sequencing (RNA-seq) data sets of lung samples from five SARS-CoV-ii patients to explore the pathophysiological effect of COVID-19 on the Hippo signaling system. The authors investigated the phosphorylation status of the Yes-associated protein (YAP) and transcriptional coactivator with postsynaptic density protein (PSD95), drosophila disc large tumor suppressor (Dlg1), and zonula occludens-ane protein (zo-one) (PDZ)-binding motif (TAZ) in SARS-CoV-2 patients and command lungs.
The apical surface of the ALI cultures was SARS-CoV-2-infected to appraise the impact of viral infection on the Hippo organization at a postal service-translational caste. SARS-CoV-two parental strains from the Biodefense and Emerging Infections Inquiry Resources Repository (BEI Resources) were used for infection experiments at the University of California, Los Angelis (UCLA) at a biosafety level 3 (BSL3) high-containment facility. Further, the Hippo signaling system in the cultured human airway epithelial cell line 3 (Calu-iii) during SARS-CoV-2 infection with the Delta variant of concern (VOC) and parental strains was assessed.
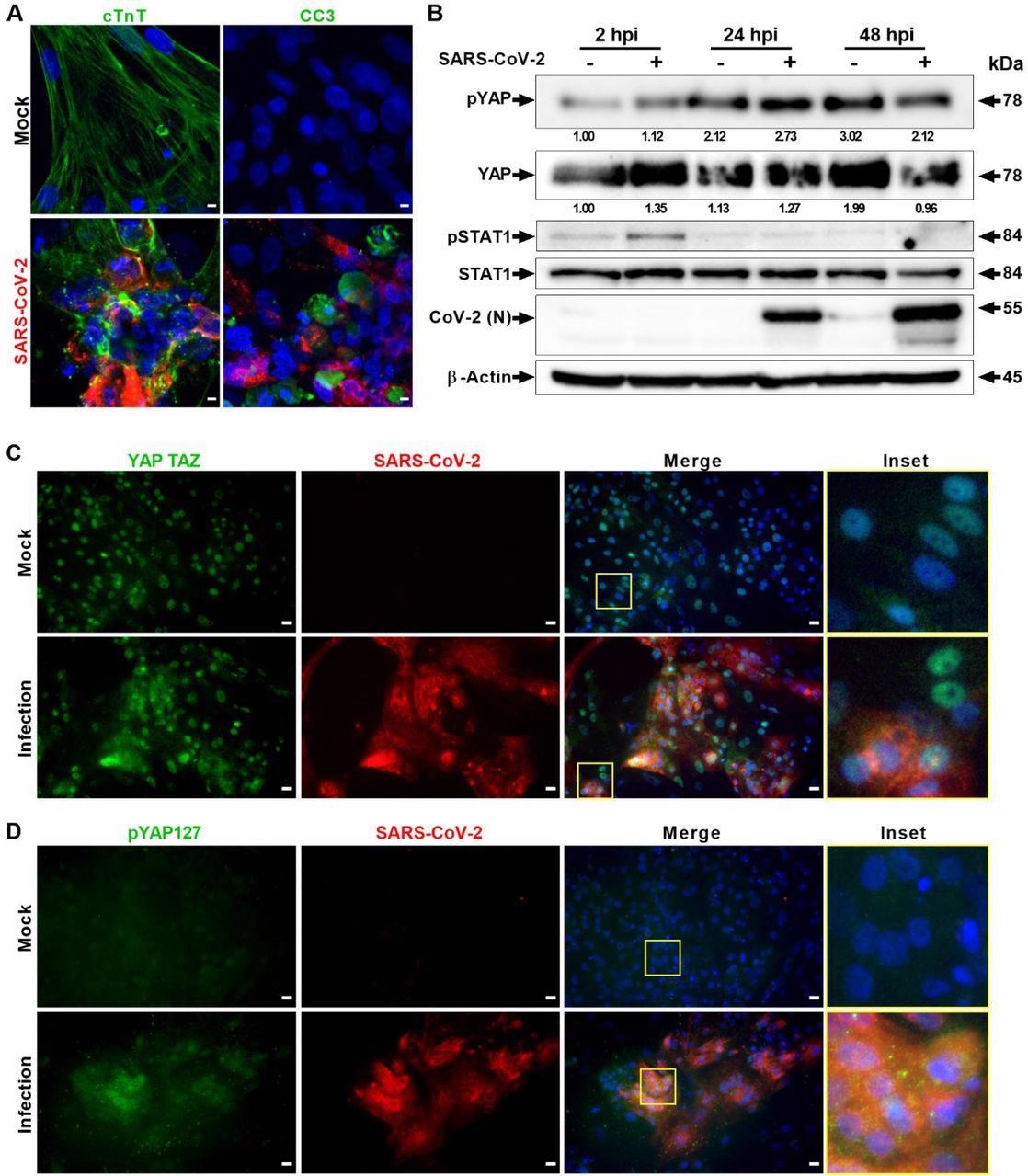
SARS-CoV-2 infection activates Hippo and antiviral STAT pathways in hPSC-CMs. (A) Confocal prototype assay of SARS-CoV-ii (red) infected cardiomyocytes shows extensive damage to cTNT positive (light-green) cells, which undergo apoptotic prison cell death (green; cleaved caspase 3). Scale bar 5 μm. north=6 independent experiments. (B) Western blot analyzes testify activation of Hippo and STAT1 pathways. Phospho-YAP127 level is increased at 2 and 24 hpi upon SARS-CoV-2 infection. Northward=2 contained experiments. (C) Immunohistochemistry analysis of SARS-CoV-2 infected PSC-CMs at 24 hpi reveals cytoplasmic localization of YAP/TAZ and (D) increase in pYAP127 level. Scale bar 25 μm.
Results and discussions
The study results showed that during SARS-CoV-two infection, 45 genes in the Hippo pathway were differentially controlled, amongst which 33 genes were upregulated, almost likely owing to antiviral host response. A downstream Hippo signaling pathway transcriptional coactivator and Yes-associated protein (YAP) homolog, WWTR1/TAZ, was significantly downregulated in COVID-19.
SARS-CoV-2 genomes were detected in the virus-infected lungs. Moreover, the lungs of the COVID-nineteen patients demonstrated a superior level of phospho-YAP at Serine 127 (Ser127) position and inflammatory cellular infiltration relative to command lungs. The heightened phospho-YAP levels at Ser127 in protein samples were procured iii- and half dozen days mail service-infection (dpi), indicating the stimulation of the Hippo signaling pathway in COVID-19. The authors also observed a concurrent stimulation of the innate immune response, shown by an increase in phospho-TANK-binding kinase i (TBK1) at Ser172.
SARS-CoV-2-infected lung ALI cultures showed that both mucus secreted and ciliated cells were infected at six dpi. Both SARS-CoV-2 Delta and parental infections in the Calu-3 cell cultures resulted in elevated phospho-YAP at Ser127. Additionally, the phospho-YAP (Ser127) poly peptide clusters developed punctate structures in the cytoplasm, probably for potential degradation in the autophagosomes.
An active Hippo signaling pathway was observed in the cardiomyocyte systems infected with SARS-CoV-two. In addition, the authors found proof of the proviral activeness of YAP/TAZ and the antiviral efficacy of large tumor suppressor 1 (LATS1) kinase.
In addition, the results indicated that the pharmacological inhibition of mammalian sterile 20-like kinases 2 and i (MST2/1) enhances the vulnerability of lung and cardiac cells to COVID-xix. Hence, LATS1/ii or MST1/2 loss of function mutations could probably elevate susceptibility to COVID-xix in humans.
Of annotation, treatment with verteporfin, a pharmacological YAP inhibitor, led to a subtract in the YAP/TAZ protein levels and SARS-CoV-2 multiplication at 48 hours post-infection in Calu-3 cells than in vehicle-treated cells.
Collectively, the data indicate that Hippo signaling has a direct antiviral role in SARS-CoV-two infection and its pathogenesis, which could be addressed therapeutically.
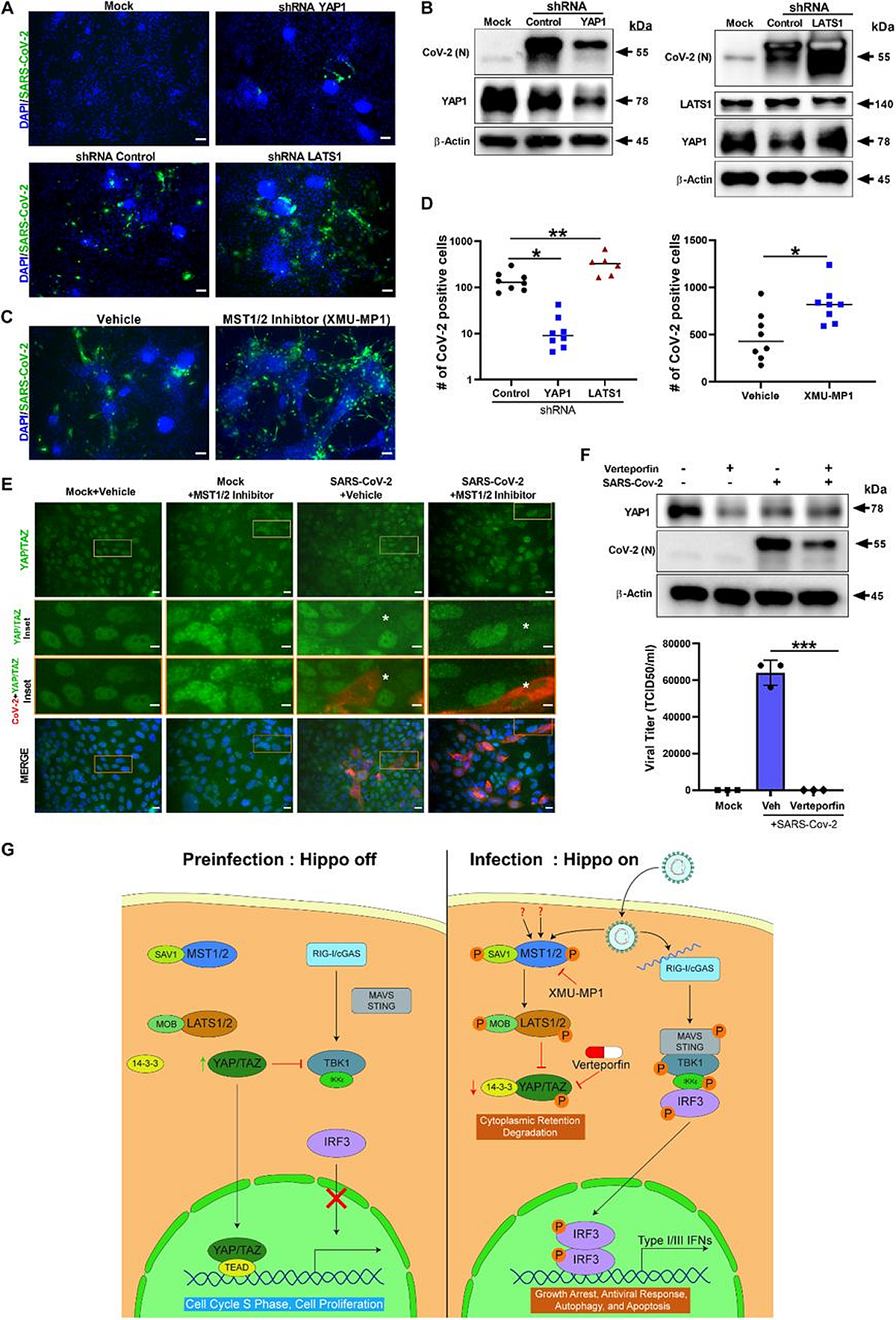
ShRNA-mediated knockdown and pharmacological modulation of SARS-CoV-two replication. (A) IHC analysis of shRNA-mediated knockdown of YAP1 and LATS1 specific shRNAs showed efficiently reduced or increased SARS-CoV-2 replication (green) relative to shRNA command, respectively in hPSC-CMs. Calibration bar 50 μm. (B) Western blot analysis of shRNA-mediated knockdown of YAP1 and LATS1 corresponding protein expression. (Con: Command shRNA). (C) IHC images of XMU-MP-ane (MST1/two inhibitor) and vehicle treated hPSC-CMs are shown. Notation: XMU-MP-1 increased SARS-CoV-2 replication (green) in hPSC-CM. (D) Graphs depict quantification of SARS-CoV-2 positive cells in infected hPSC-CM respective to panels A and C. Student T-test. **P >0.001. n=2 contained experiments. (E) IHC Images show YAP/TAZ protein (green) and SARS-CoV-2 Spike (ruddy) in Calu-3cells. Annotation, MST1/ii inhibitor treated Calu-three cells have higher number of infected cells. Inset and white asterisk hovers infected cells showing depletion of YAP/TAZ. Scale bar: 25 μm. Inset scale bar ten μm. (F) Western blot analysis of Calu-three cells treated with Verteporfin (1μM) and SARS-CoV-2 infection. Drug treatment resulted in reduction in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Graph shows the viral titer (TCID50/ml) measurement of infected also every bit treated Calu-iii culture supernatant(representative data from ii independent experiments) (G) Schematic diagram of our hypothetical model integrating Hippo and TBK1 signaling pathways during preinfection (Hippo off) and SARS-CoV-two infection states (Hippo on). c-GAS, circadian GMP-AMP synthase; IKKe, inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B kinase subunit epsilon; MAVS, mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein; RIG-I, retinoic acid-inducible cistron I poly peptide; STING, stimulator of interferon response cGAMP interactor i; TEAD, TEA domain transcription factors.
Conclusions
The written report findings unraveled that the evolutionarily conserved Hippo signaling pathway plays a vital role in the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infection. In thein vitrocultures and lungs, SARS-CoV-2 infection activated the Hippo signaling organization. The Hippo pathway was stimulated past both the SARS-CoV-2 Delta VOC and parental strain infections. In add-on, SARS-CoV-2 replication was considerably boosted afterward cistron knockdown and chemic inhibition of upstream kinases LATS1 and MST1/ii, marking their antiviral functions. Verteporfin, a pharmacological inhibitor of YAP, the Hippo pathway downstream transactivator, considerably hindered SARS-CoV-2 replication.
Notably, the researchers stated that i) further mechanistic experiments are necessary to delineate the base of the Hippo pathway function in antiviral responses to RNA viruses and 2) preclinical animal efficacy and safety evaluations of verteporfin handling for SARS-CoV-two infection are required in the hereafter.
Overall, the present piece of work showed that Hippo signaling has a directly antiviral function in SARS-CoV-2 infection and offered a new option for pharmacologically targeting this pathway to treat COVID-19.
*Important find
bioRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not exist regarded as conclusive, guide clinical practise/wellness-related behavior, or treated equally established information.
Journal reference:
- Hippo Signaling Pathway Activation during SARS-CoV-two Infection Contributes to Host Antiviral Response; Gustavo Garcia Jr., Yijie Wang, Joseph Ignatius Irudayam, Arjit Vijey Jeyachandran, Sebastian Castillo Cario, Chandani Sen, Shen Li, Yunfeng Li, Ashok Kumar, Karin Nielsen-Saines, Samuel W. French, Priya S. Shah, Kouki Morizono, Brigitte Gomperts, Arjun Deb, Arunachalam Ramaiah, Vaithilingaraja Arumugaswami, bioRxiv preprint 2022, DOI: https://doi.org/ten.1101/2022.04.07.487520, https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.04.07.487520v1
Source: https://www.news-medical.net/news/20220411/Scientists-find-critical-role-for-Hippo-signaling-pathway-in-COVID-19-pathogenesis.aspx
Posted by: smoothitery.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Type Of Animal Is A Hippo"
Post a Comment